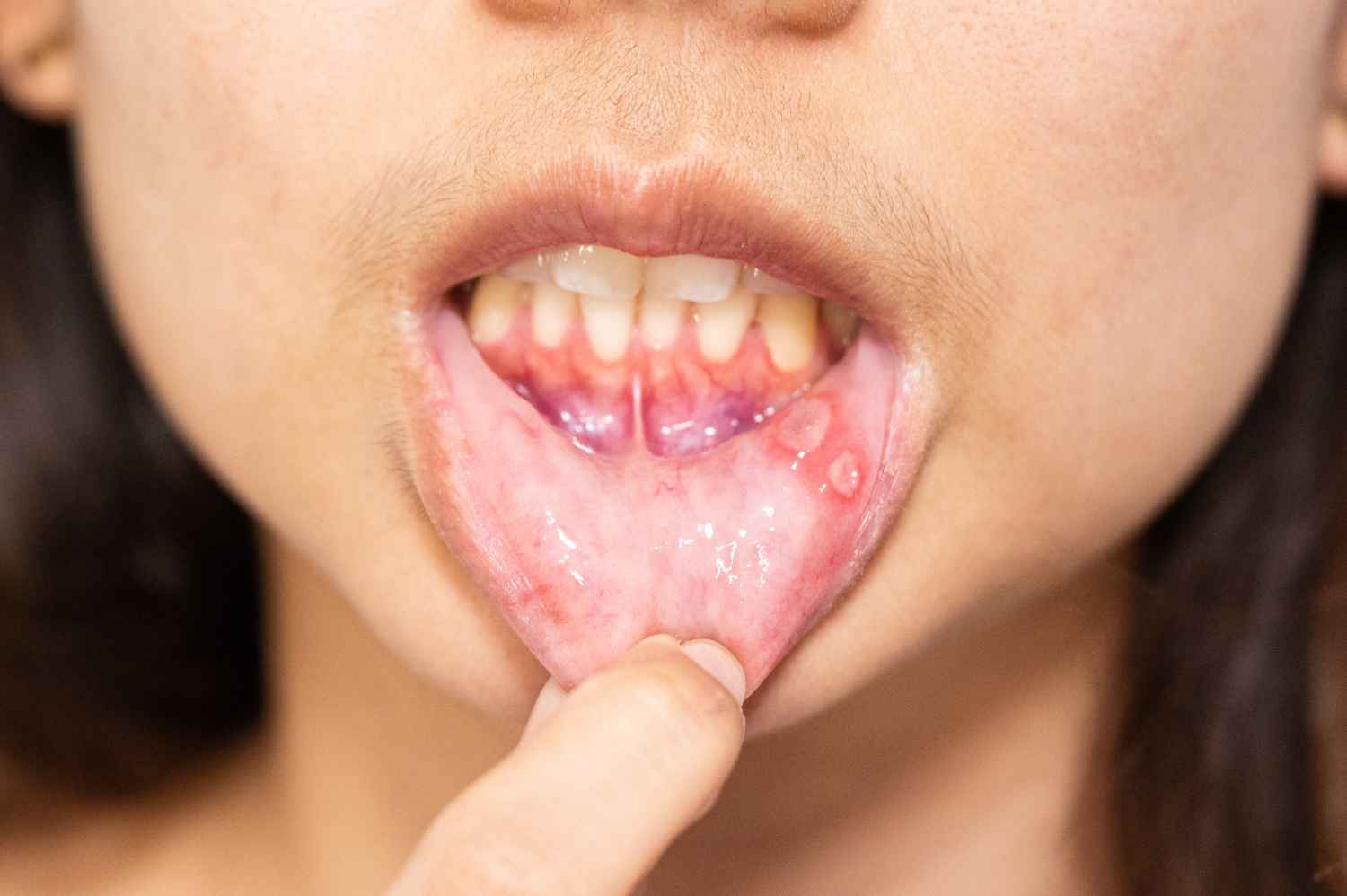
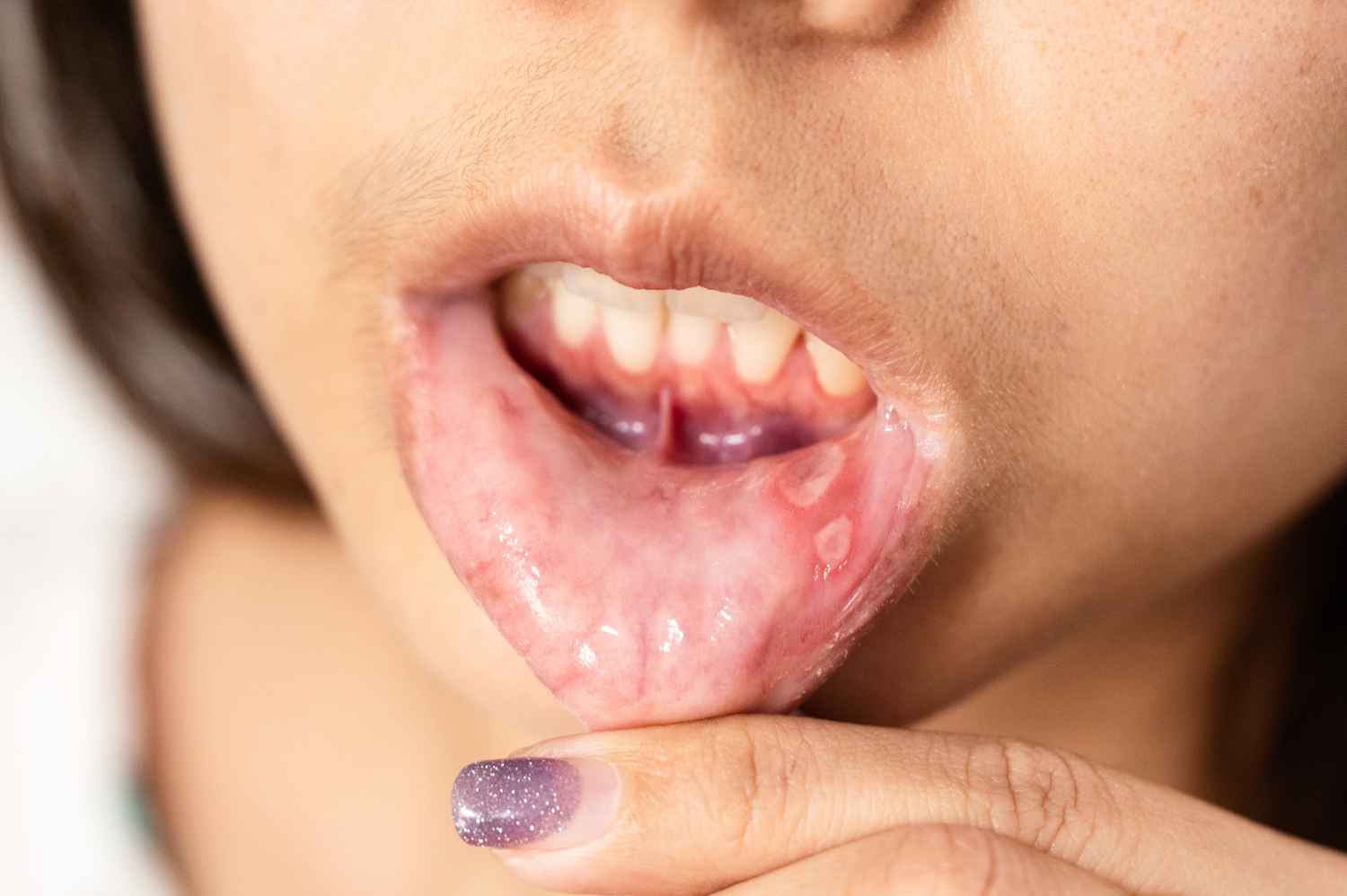
Your mouth is the gateway to your overall health — and when infections strike, they can do more harm than you might realise. From mild gum irritation to severe abscesses that affect the jaw and bloodstream, mouth infections can quickly escalate if left untreated.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments of mouth infections can help you take action before they become serious. Let’s explore everything you need to know — and when it’s time to see a dentist.
What Are Mouth Infections?
A mouth infection occurs when harmful bacteria, viruses, or fungi invade the tissues of your mouth — including the gums, teeth, tongue, or inner cheeks. These infections can lead to pain, swelling, bleeding, and even systemic health problems if not addressed in time.
Common types of mouth infections include:
- Gum infections (Gingivitis & Periodontitis)
- Tooth infections (Dental Abscesses)
- Viral infections (Cold sores, Herpes simplex virus)
- Fungal infections (Oral Thrush)
- Tonsil or throat infections
- Post-procedure infections (after tooth extraction or implants)
Each type requires a different treatment approach, but they all share one rule: early detection is key.
Common Symptoms of Mouth Infections
Mouth infections may start small — but their symptoms can quickly worsen. Here are the warning signs to look out for:
1. Persistent Pain or Swelling
Pain in your gums, teeth, or jaw is often one of the first signs. If swelling accompanies it, it could indicate a tooth abscess or gum infection.
2. Bleeding Gums
Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing may be showing early signs of gingivitis — the first stage of gum disease.
3. Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Chronic bad breath, even after brushing, can be a red flag for bacterial buildup or infection.
4. White or Red Patches
White patches may suggest oral thrush, while red, inflamed areas can indicate viral or bacterial infections.
5. Difficulty Chewing or Swallowing
Infections can cause inflammation that makes eating or swallowing painful — especially in the throat or tonsils.
6. Pus or Abscess Formation
A pimple-like bump on the gums or near a tooth usually points to an abscess, which can spread infection to other parts of the body if untreated.
7. Fever or Fatigue
A severe infection may trigger your body’s immune response, causing fever and general weakness.
What Causes Mouth Infections?
Several factors can trigger infections in the mouth. Understanding these helps in both prevention and timely treatment.
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Not brushing or flossing properly allows plaque to build up, creating a breeding ground for bacteria that cause gum disease and tooth decay.
2. Untreated Cavities
When cavities deepen, bacteria can reach the tooth pulp, leading to painful tooth abscesses.
3. Weak Immune System
Individuals with diabetes, autoimmune conditions, or those undergoing chemotherapy are more vulnerable to oral infections.
4. Viral or Fungal Exposure
Viruses like herpes simplex and fungi such as Candida albicans can cause recurrent oral infections.
5. Dental Procedures
Improper post-procedure care after tooth extraction, implants, or root canals can sometimes lead to infection.
6. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco weakens gum tissue and lowers your mouth’s ability to fight infections.
7. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
A lack of saliva reduces natural cleansing, allowing bacteria to multiply.
Common Types of Mouth Infections
1. Gingivitis
- Cause: Plaque buildup and poor oral hygiene
- Symptoms: Red, swollen, bleeding gums
- Treatment: Professional cleaning and improved brushing habits
2. Periodontitis
- Cause: Untreated gingivitis
- Symptoms: Gum recession, loose teeth, bad breath
- Treatment: Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), antibiotics, or surgery
3. Dental Abscess
- Cause: Bacterial infection at the root of a tooth
- Symptoms: Throbbing pain, swelling, and pus discharge
- Treatment: Drainage, root canal, or tooth extraction
4. Oral Thrush
- Cause: Overgrowth of Candida fungus
- Symptoms: White patches, soreness, burning sensation
- Treatment: Antifungal mouthwash or tablets
5. Cold Sores
- Cause: Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)
- Symptoms: Fluid-filled blisters on the lips or gums
- Treatment: Antiviral creams or oral medications
Effective Treatments for Mouth Infections
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection. Here’s how dental professionals typically address them:
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
Removes plaque, tartar, and bacteria from below the gum line — the root cause of many gum infections.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
Dentists may prescribe antibiotics (like amoxicillin or metronidazole) for bacterial infections or antifungals for oral thrush.
3. Root Canal Therapy
For tooth abscesses, a root canal removes the infected pulp and saves the natural tooth.
4. Drainage of Abscess
In severe infections, the dentist may drain the pus to relieve pain and pressure.
5. Surgical Intervention
Advanced cases of periodontitis may require flap surgery or tissue grafts to restore gum health.
6. Pain Relief and Home Care
Dentists often recommend pain relievers, saltwater rinses, and antiseptic mouthwashes as part of ongoing care.
Home Remedies for Mild Mouth Infections (With Caution)
While professional dental care is essential, these home remedies can support healing:
- Saltwater rinse: Mix ½ tsp of salt in warm water and rinse twice daily.
- Hydrogen peroxide rinse: Kills bacteria (use diluted, and never swallow).
- Clove oil: Natural antibacterial that soothes tooth pain.
- Cold compress: Helps reduce swelling and pain.
- Maintain hydration: Saliva naturally fights bacteria.
Note: Home remedies can relieve mild symptoms, but do not replace dental treatment. Always see your dentist if symptoms persist beyond two days.
Prevention: How to Avoid Mouth Infections
The best way to handle mouth infections is to prevent them before they start.
- Brush twice daily using fluoride toothpaste
- Floss once daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash
- Visit your dentist every 6 months for check-ups
- Avoid smoking and tobacco
- Eat a balanced diet with plenty of vitamins and minerals
- Stay hydrated to maintain saliva flow
When to See a Dentist Immediately
You should contact your dentist right away if you experience:
- Severe or spreading pain
- Swelling in the face or jaw
- Fever or fatigue accompanying mouth pain
- Pus or abscess formation
- Difficulty opening your mouth or swallowing
Ignoring these signs can lead to serious complications, such as jawbone infection or even sepsis.
The Connection Between Oral and Overall Health
Recent studies show that untreated oral infections can contribute to systemic conditions such as:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Respiratory infections
- Preterm birth (in pregnant women)
This makes dental hygiene not just about a beautiful smile — but about protecting your total health.
Conclusion
Mouth infections are more than just a minor inconvenience. Whether it’s a gum issue, tooth abscess, or fungal infection, ignoring the early signs can lead to serious health risks.
At Smiline Dental Hospitals, our expert dentists use advanced diagnostic tools and gentle care to detect, treat, and prevent all types of oral infections. Don’t wait for pain to worsen — early treatment ensures faster recovery and lasting oral health